Taylor Scott International News
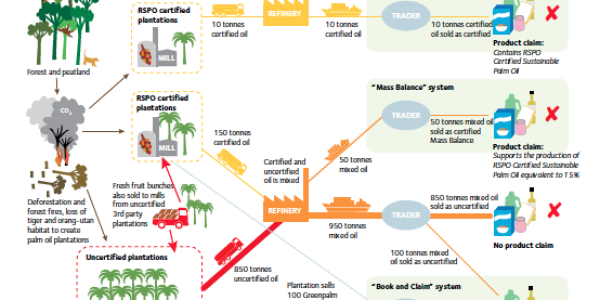
New report by Greenpeace details the failure of RSPO in halting deforestation, and highlights Wilmar, Genting and Surya Dumai as firms with concessions behind the recent haze crisis in Singapore and Malaysia The palm oil industry is destroying Indonesia’s forests, said Greenpeace International in a new report on Tuesday, as the Roundtable for Sustainable Palm Oil (RSPO) is set to meet for its first European Summit in Berlin. In the investigative paper, “Certifying Destruction”, Greenpeace higlighted the failure of the sustainable palm oil and certification body in halting deforestation. RSPO concessions accounted for as much as 39 per cent of the fire hotspots on palm oil concessions in Riau during January to June 2013, when the most severe haze outbreak in history affected neighbouring Singapore and Malaysia. The report, which gives a mapping anaylsis of the concessions, charged that RSPO standards are severely lacking, leaving members “free to destroy forests” that contribute to more greenhouse gas emissions, human rights violations, loss of endangered species such as the Sumatran tiger and orang-utan and the Borneo orang-utan, and the yearly regional haze. RSPO members account for about 40 per cent of global palm oil production. With the launch of the report, Greenpeace is calling for the industry, especially those gathering at the summit, where the future of palm oil sustainability will be discussed, to take action against deforestation. Bustar Maitar, Greenpeace International’s head for the Indonesia Forest Campaign, told Eco-Business: “We want to see the companies, palm oil producers and the buyers to act more to stop deforestation … We want to see the customers make sure that their product is not associated with deforestation. Customers can’t just say that because they are buying from RSPO companies then they have no relation with deforestation and peat land destruction…” According to Indonesia’s Ministry of Forestry maps, the country has lost 1.24 million hectares of forest from 2009 to 2011. In the same period, about 300,000 hectares or a quarter of this total forest loss was due to identified palm oil concessions, said Greenpeace, making the palm oil sector the largest driver of forest destruction in Indonesia. Illegal land clearing and unsustainable sourcing “ Even among the RSPO’s own members, dirty palm oil remains the common currency – RSPO standards are inadequate, poorly enforced and offer palm oil consumers no guarantee that the oil they buy has been produced responsibly Greenpeace International “Year after year, Indonesia’s forest fires and haze wreak havoc on the region, and the palm oil sector is a main culprit,” said Maitar. He added, “While RSPO members might have no-fire policies, the peat land they have cleared and drained is like a tinderbox – one spark is all it takes.” According to anaylsis by Greenpeace, Singapore-based Wilmar International, the world’s largest palm oil trader, along with Genting and Surya Dumai, are “the three privately-owned RSPO members with the largest areas of identified deforestation”. Wilmar prohibits burning on its own plantations, but it sources more than 90 per cent of its crude palm oil from third-party suppliers. Some of palm oil products it has received come from illegal plantations inside the Tesso Nilo National Park in Riau as recently as 2012, according to a WWF investigation, cited the Greenpeace report. While the agribusiness firm denied this and mentioned of procedures stopping such practices, the lax criteria on third-party supply does not promote the strict use of clean palm oil into global supplies, said Greenpeace. This fresh fruit bunch (FFB) or palm oil products sourced from third-party suppliers could have been produced through illegal land clearing, they added. Inadequacies of RSPO The RSPO lacks standards encouraging transparency in sourcing or mechanisms that offer traceability throughout the entire palm oil supply chain, from plantation to the end consumer product sold on supermarkets and other retail stores. The report showed a visual flowchart of the RSPO supply chain illustrating three different supply systems – segregated supply, mass balance, and book and claim – that translate to different palm oil products, as well as different claims of palm oil certification. “Even among the RSPO’s own members, dirty palm oil remains the common currency – RSPO standards are inadequate, poorly enforced and offer palm oil consumers no guarantee that the oil they buy has been produced responsibly,” said Greenpeace. In fact, of the 250 palm oil consumer companies interviewed by the environmental group , those who replied stated they still rely on RSPO’s sustainability measures. Procter and Gamble, one of the respondents, said, “By 2015, 100 per cent of our palm oil purchases will be confirmed to have originated from responsible and sustainable sources… [We are] aiming to source certified sustainable palm oil and PKO (palm kernel oil) via the RSPO Mass Balanced Supply Chain model, but will also be source via the Book and Claim model.” However, Greenpeace emphasised that the RSPO is “not fit for this purpose”. The report outlines how the RSPO faces criticism from consumer companies and non-government organisations, despite having recently revised its principles and criteria and having the support of the Consumer Goods Forum and the Sustainable Palm Oil Investor Working Group. Kellogg, the company behind well-known cereals and energy bars, recently received backlash from consumer activist group Sum of Us due to its joint venture with Wilmar International. Campaign director Rob Wohl, in an article with trade website Bakery and Snacks, said, “Sourcing RSPO-certified palm oil is nice, but Kellogg’s (and really, all global corporations) need to be doing everything in their power to stop deforestation. Ideally, Kellogg should follow Nestlé’s lead by adopting strong deforestation-free principles and allow independent oversight of its supply chain.” Going beyond the RSPO Greenpeace likewise named the Swiss multinational company as an example of a consumer goods firm that has taken palm oil sustainability seriously. The environmental NGO, back in 2010, lambasted the firm’s use of unsustainable palm oil from Indonesian supplier Sinar Mas for its Kit Kat chocolate bar. Since then, Nestlé has addressed its sourcing, even including a goal on the use of sustainable palm oil by end of the year on its list of published environmental targets for 2020. Golden Agri-Resources, New Britain Palm Oil and Agropalma are the other exemplary companies cited by Greenpeace in the report. According to Areeba Hamid, the NGO’s forest campaigner, “The only solution for palm oil consumers and producers is to go beyond the RSPO – as some members are doing already. This is the challenge we set to the industry.” The Palm Oil Innovation Group, an initiative by some palm oil firms and NGOs including Greenpeace, is an example of industry efforts outside the RSPO. The group is for the conservation of high carbon stock forests and also secondary forests, which the RSPO does not protect in its stipulated forest clearance ban. Greenpeace, in the report, recommended what other actions the RSPO should take to improve its standards. They also listed their solutions and demands for palm oil consumer companies, traders and processors, and producers. Hamid said, “Brands must find out where their palm oil comes from, and guarantee consumers around the world that forest destruction is not making its way into our products.” Wilmar, as well as Golden Agri and Kuala Lumpur Kepong Bhd (KLK), showed that having questionable business operations has repercussions. Norway’s sovereign wealth fund, the richest in the world at US$737 billion, sold its investments in the palm oil producers last 2012, citing concerns on deforestation. Taylor Scott International
Taylor Scott International, Taylor Scott